Qualification of Micronized Kyanite and Silica Fume
Materials Science & Technology 2006; October 15-18, 2006 — Cincinnati, OH, USA
William L. Headrick,
Missouri Refractories Co., Inc., Formerly University of Missouri-Rolla
Co-Authors
Dilip Jain, Kyanite Mining Corp.
Musa Karakus, University of Missouri-Rolla
Participants
West Virginia University (WVU):Corrosion and Evaluation of Metallic Materials, Dross Buildups/Corrosion in GI/GL
University of Missouri-Rolla (UMR):Selection and formulation of Refractory Materials for Molten metal application, Corrosion testing and Post-mortem analysis
Oak Ridge National Laboratories (ORNL):Design, FEA Modeling, Measurement of Thermo-Physical properties
Industry Participants: Refractory manufacturers, Specialty metal smelters, Aluminum smelters, Steel manufacturers
Abstract
Micronized kyanite is a new raw material available from Virginia Kyanite. It has a mean particle size less than 5 microns and thus can be used to efficiently increase the ultra-fines concentration of self-flow and vibratable castables. Especially those castables used in secondary aluminum manufacturing. The University of Missouri-Rolla has shown that kyanite is more resistant to aluminum attack than silica, mullite and bauxite through post mortems. They have also shown that use of silica fume as an ultra-fine additive and flow aid leads to accelerated reactions with molten aluminum. Characterization of micronized kyanite with a comparison to fume silica is given. It is proposed that micronized kyanite may be used as a partial or total replacement for ultra-fine silica and alumina additions.
Introduction
Ref. M. Karakus,W. L. Headrick, and E. Feiner, “Aluminum Melting Furnace Post-Mortem”, pp. 135-156, in Monolithics: Advances, Installation and “Boom”, 41st Symposium on Refractories, The American Ceramic Society, March 30-31st, 2005, St. Louis.
Musa Karakus, UMR, found that kyanite crystals were least attacked by molten aluminum of any refractory grain.
Aluminum Attack Findings
Purity and type (sintered or single crystal) of refractory fillers play an important role for the reduction of refractory aggregates by molten aluminum.
Silica fume is the initial path of aluminum attack.
All bauxite derived alumina aggregates were destroyed by molten aluminum due to Fe-Ti and K-Na-rich glassy grain boundary matrix.
Selective reduction of mullite aggregates was observed.
Single kyanite grains are observed to be unaffected by molten metal penetration into castable.
Destruction of mullite and alumina
Development of castables using micronized kyanite
1.Prepare castables by partial replacement of fumed silica with micronized kyanite such that flow is maintained.
2.Replace bauxite, tabular, flint clay, or mullite fines with kyanite.
Samples
•Micronized Kyanite, Kyanite Mining
•ES 900 W Lot# 217, Elkem
•965 Fume Silica Controlled Density, Elkem
•T-500 Silica Fume Lot# FZ6A23-1,
•8010 Globe Silica Fume Regular, Globe Metallurgical
•D1000 Amorphous Silica Fume, Technical Silica Company
Mix 2 grams powder with 20 ml water. Wait 3 minutes then measurepH.
pH
Powders rapidly settled out of water after agitation with the exception of 8010.
8010 remains suspended in water for days.
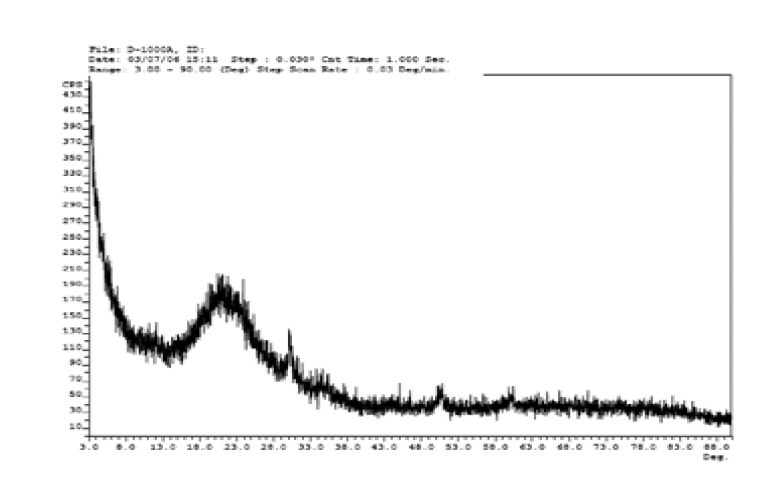
XRD of Micronized Kyanite and Fume Silica
Micronized Kyanite contains almost no amorphous phase.
XRD-Silica Fume
Thermogravimetric Analysis
Scanning Electron Microscopy
Particle Size Distribution
Micronized Kyanite
Mean Agglomerate Size 5 micron
Mean Particle Size 5 micron
Fumed Silica
Mean Agglomerate Size 50 micron
Mean Particle Size 0.1 micron
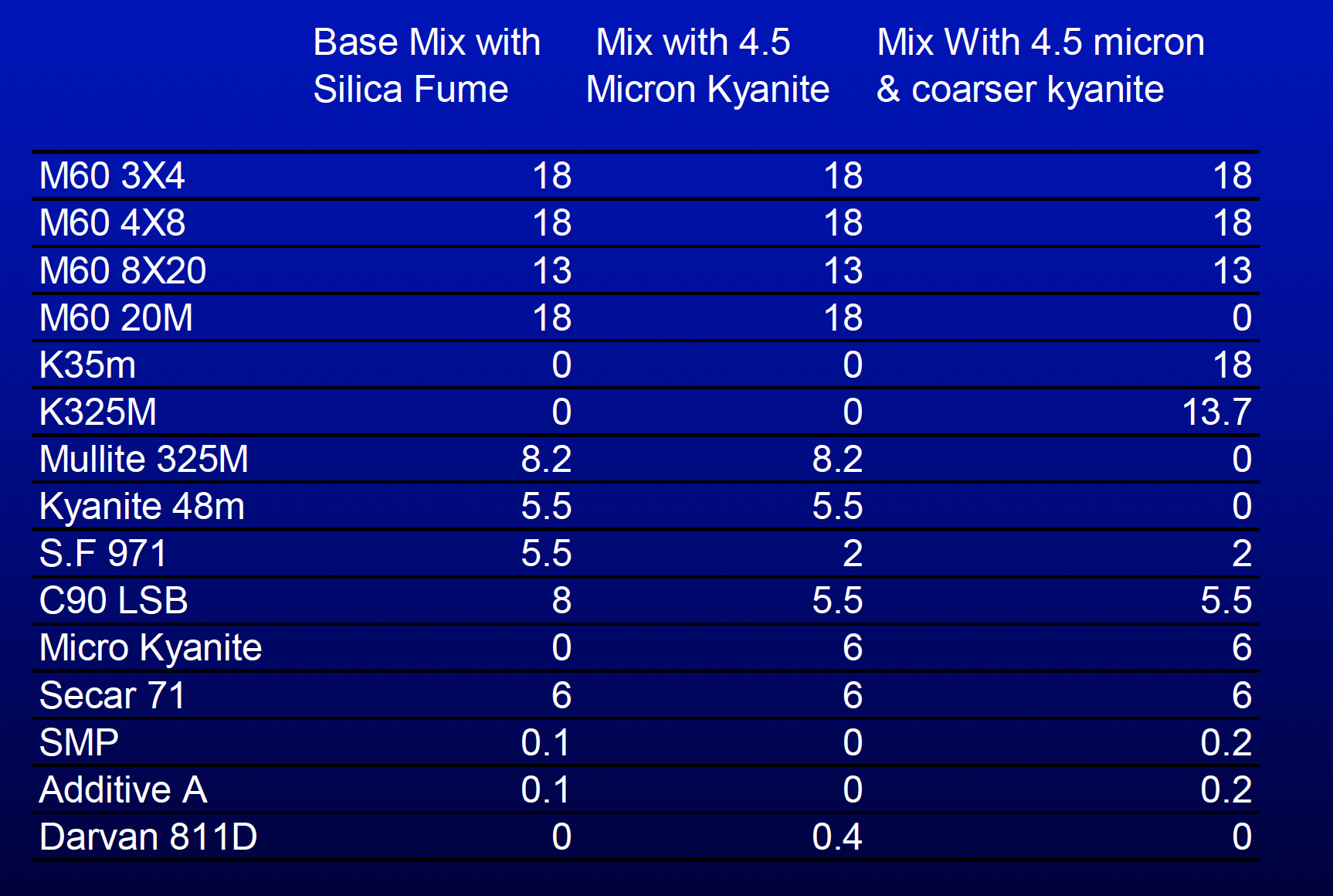
Trial Mixes
Chemistry
Properties
Cup Test Results
Test parameters:
Duration: 240 hours (10 days) at 1000°C
Pre-oxidized to 1200°C for 5 hours
Steam atmosphere maintained during test.
Tested for penetration resistance to molten Al alloy
Cup Test Results
Order of attack:
Mullite
Matrix
Kyanite (grain boundary attack)
Micronized kyanite
Conclusion
Micronized Kyanite can be used as a partial replacement for fume silica.
Flow is lower with micronized kyanite.
Corrosion resistance against aluminum metal is greatly increased by using kyanite versus Mulcoa 60 fines.
DISCLAIMER
This report was prepared as an account of work sponsored by an agency of the United States Government. Neither the United States Government nor any agency thereof, nor any of their employees, makes any warranty, express or implied, or assumes any legal liability or responsibility for the accuracy, completeness, or usefulness of any information, apparatus, product, or process disclosed, or represents that its use would not infringe privately owned rights. Reference herein to any specific commercial product, process, or service by trade name, trademark, manufacturer, or otherwise does not necessarily constitute or imply its endorsement, recommendation, or favoring by the United States Government or any agency thereof. The views and opinions of authors expressed herein do not necessarily state or reflect those of the United States Government or any agency thereof.
Funded by
DOE Award No. DE-FC36-04GO14038
Kyanite Mining Corporation
Missouri Refractories Co., Inc.